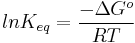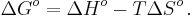Strain (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule experiences strain when its chemical structure undergoes some stress which raises its internal energy in comparison to a strain-free reference compound. The internal energy of a molecule consists of all the energy stored within it. A strained molecule has an additional amount of internal energy which an unstrained molecule does not. This extra internal energy, or strain energy, can be likened to a compressed spring.[1] Much like a compressed spring must be held in place to prevent release of its potential energy, a molecule can be held in an energetically unfavorable conformation by the bonds within that molecule. Without the bonds holding the conformation in place, the strain energy would be released.
Contents |
Summary
Thermodynamics
The equilibrium of two molecular conformations is determined by the difference in Gibbs free energy of the two conformations. From this energy difference, the equilibrium constant for the two conformations can be determined.
If there is a decrease in Gibbs free energy from one state to another, this transformation is spontaneous and the lower energy state is more stable. A highly strained, higher energy molecular conformation will spontaneously convert to the lower energy molecular conformation.
Enthalpy and entropy are related to Gibbs free energy through the equation
Enthalpy is typically the more important thermodynamic function for determining a more stable molecular conformation.[1] While there are different types of strain, the strain energy associated with all of them is due to the weakening of bonds within the molecule. Since enthalpy is usually more important, entropy can often be ignored.[1] This isn't always the case; if the difference in enthalpy is small, entropy can have a larger say in the equilibrium. For example, n-butane has two possible conformations, anti and gauche. The anti conformation is more stable by 0.9 kcal/mol.[1] We would expect that butane is roughly 82% anti and 18% gauche at room temperature. However, there are two possible gauche conformations and only one anti conformation. Therefore, entropy makes a contribution of 0.4 kcal in favor of the gauche conformation.[2] We find that the actual conformational distribution of butane is 70% anti and 30% gauche at room temperature.
Determining molecular strain
The heat of formation (ΔHfo) of a compound is described as the enthalpy change when the compound is formed from its separated elements.[3] When the heat of formation for a compound is different from either a prediction or a reference compound, this difference can often be attributed to strain. For example, ΔHfo for cyclohexane is -29.9 kcal/mol while ΔHfo for methylcyclopentane is -25.5 kcal/mol.[1] Despite having the same atoms and number of bonds, methylcyclopentane is higher in energy than cyclohexane. This difference in energy can be attributed to the ring strain of a five-membered ring which is absent in cyclohexane. Experimentally, strain energy is often determined using heats of combustion which is typically an easy experiment to perform.
Determining the strain energy within a molecule requires knowledge of the expected internal energy without the strain. There are two ways do this. First, one could compare to a similar compound that lacks strain, such as in the previous methylcyclohexane example. Unfortunately, it can often be difficult to obtain a suitable compound. An alternative is to use Benson group increment theory. As long as suitable group increments are available for the atoms within a compound, a prediction of ΔHfo can be made. If the experimental ΔHfo differs from the predicted ΔHfo, this difference in energy can be attributed to strain energy.
Kinds of strain
Van der Waals strain
Van der Waals strain, or steric strain, occurs when nonbonded atoms are forced closer to each other than their Van der Waals radii allow. Specifically, Van der Waals strain is considered a form of strain where the interacting atoms are at least four bonds away from each other.[4] The amount on steric strain in similar molecules is dependent on the size of the interacting groups; bulky tert-butyl groups take up much more space than methyl groups and often experience greater steric interactions.
The effects of steric strain in the reaction of trialkylamines and trimethylboron were studied by Brown et al.[5] They found that as the size of the alkyl groups on the amine were increased, the equilibrium constant decreased as well. The shift in equilibrium was attributed to steric strain between the alkyl groups of the amine and the methyl groups on boron.
Syn-pentane strain
There are situations where seemingly identical conformations are not equal in strain energy. Syn-pentane strain is an example of this situation. There are two different ways to put both of the bonds the central in n-pentane into a gauche conformation, one of which is 3 kcal/mol higher in energy than the other.[1] When the two methyl-substituted bonds are rotated from anti to gauche in opposite directions, the molecule assumes a cyclopentane-like conformation where the two terminal methyl groups are brought into proximity. If the bonds are rotated in the same direction, this doesn't occur. The steric strain between the two terminal methyl groups accounts for the difference in energy between the two similar, yet very different conformations.
Allylic strain
Allylic strain, or A1,3 strain is closely associated to syn-pentane strain. An example of allylic strain can be seen in the compound 2-pentene. It's possible for the ethyl substituent of the olefin to rotate such that the terminal methyl group is brought near to the vicinal methyl group of the olefin. These types of compounds usually take a more linear conformation to avoid the steric strain between the substituents.[1]
1,3-diaxial strain
1,3-diaxial strain is another form of strain similar to syn-pentane. In this case, the strain occurs due to steric interactions between a substituent of a cyclohexane ring and a hydrogen at the meta position. When the substituent is axial, it is brought near to an axial meta hydrogen. The amount of strain is largely dependent on the size of the substituent and can be relieved by forming the other chair conformation which puts the substituent in an equatorial position. The difference in energy between conformations is called the A value and is well known for many different substituents.
Torsional strain
Torsional strain is the resistance to bond twisting. In cyclic molecules, it is also called Pitzer strain.
Torsional strain occurs when atoms separated by three bonds are placed in an eclipsed conformation instead of the more stable staggered conformation. The barrier of rotation between staggered conformations of ethane is approximately 3.0 kcal/mol.[1] It was initially believed that the barrier to rotation was due to steric interactions between vicinal hydrogens, but the Van der Waals radius of hydrogen is too small for this to be the case. Recent research has shown that the staggered conformation may be more stable due to a hyperconjugative effect.[6] Rotation away from the staggered conformation interrupts this stabilizing force.
More complex molecules, such as butane, have more than one possible staggered conformation. The anti conformation of butane is approximately 3.8 kcal/mol more stable than the gauche conformation.[1] Both of these staggered conformations are much more stable than the eclipsed conformations. Instead of a hyperconjugative effect, such as that in ethane, the strain energy in butane is due to both steric interactions between methyl groups and angle strain caused by these interactions.
Angle strain
According to the VSEPR theory of molecular bonding, the preferred geometry of a molecule is that in which both bonding and non-bonding electrons are as far apart as possible. In molecules, it's quite common for these angles to be somewhat compressed or expanded compared to their optimal value. This strain is referred to as angle strain, or Baeyer strain.[7] The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane, which are discussed below.
Ring strain
Cyclic structures differ from acyclic structures in that atoms located in the ring are constrained and, except in cyclohexanes, cannot assume the preferred bond angles. Furthermore, there is often eclipsing in cyclic systems which cannot be relieved. The following table lists some common rings and their associated strain.[1]
| Number of carbons in ring | Strain energy (kcal/mol) | Number of carbons in ring | Strain energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 27.5 | 10 | 12.4 |
| 4 | 26.3 | 11 | 11.3 |
| 5 | 6.2 | 12 | 4.1 |
| 6 | 0.1 | 13 | 5.2 |
| 7 | 6.2 | 14 | 1.9 |
| 8 | 9.7 | 15 | 1.9 |
| 9 | 12.6 | 16 | 2.0 |
Small Rings
Cyclohexane is considered a benchmark in determining ring strain in cycloalkanes and it is commonly accepted that here is little to no strain energy.[1] In comparison, smaller cycloalkanes are much higher in energy due to increased strain. Cyclopropane is analogous to a triangle and thus has bond angles of 60°, much lower than the preferred 109.5° of an sp3 hybridized carbon. Furthermore, the hydrogens in cyclopropane are eclipsed. Cyclobutane experiences similar strain, with bond angles of approximately 88° (it isn't completely planar) and eclipsed hydrogens. The strain energy of cyclopropane and cyclobutane are 27.5 and 26.3 kcal/mol, respectively.[1] Cyclopentane experiences much less strain, mainly due to torsional strain from eclipsed hydrogens, and has a strain energy of 6.2 kcal/mol.
Transannular strain
Perhaps surprisingly, medium sized rings (between 7-13 carbons) experience more strain energy than cyclohexane. This transannular strain occurs when the cycloalkanes attempt to avoid angle and torsional strain. In doing so, methylene groups across from each other are brought into proximity and experience Van der Waals strain.
Bicyclic systems
The amount of strain energy in bicyclic systems is commonly the sum of the strain energy in each individual ring.[1] This isn't always the case, as sometimes the fusion of rings induces some extra strain.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Anslyn and Dougherty, Modern Physical Organic Chemistry, University Science Books, 2006, ISBN 978-1891389313
- ^ Coxon and Norman, Principles of Organic Synthesis, 3rd ed., Blackie Academic & Pro., 1993, ISBN 978-0751401264
- ^ Levine, Physical Chemistry, 5th ed., McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 978-0072534955
- ^ Brown, Foote, and Iverson, Organic Chemistry, 4th ed., Brooks/Cole, 2005, ISBN 978-0534467739
- ^ Brown, H.C.; Johannesen, R.B. (1952). "Dissociation of the Addition Compounds of Trimethlboron with n-Butyl- and Neopentyldimethylamines; Interaction of Trimethylboron and Boron Trifluoride with Highly Hindered Bases". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75: 16–20. doi:10.1021/ja01097a005.
- ^ Weinhold, F. (2001). "Chemistry: A New Twist on Molecular Shape". Nature 411 (6837): 539–541. doi:10.1038/35079225. PMID 11385553.
- ^ Wiberg, K. (1986). "The Concept of Strain in Organic Chemistry". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 25 (4): 312–322. doi:10.1002/anie.198603121.